I have a very basic understanding of Active Directory, sometimes that’s enough to get by, and sometimes it’s not. Below are some notes I took to help with the basic understanding as well as some more advanced principals. These notes will not make you go from “0 -> Hero” but should help you on your way to a better understanding of the Windows Architecture. DISCLAIMER - I am not a sysadmin, nor am I trying to come off as one, the below are just notes taken to help my understanding on the topic.
What We’ll Cover
- What is Active Directory?
- Active Directory Logical Structure
- Active Directory Services
- Other Key AD Terms
What is Active Directory?
Active Directory, commonly referred to as AD - is, at its core, a database. This database holds information regarding domains, users, and objects within a network. The individual who maintains the “database” (usually a System Administrator) creates groups and subgroups to organize those users and objects, providing access control at each level.
Active Directory Logical Structure
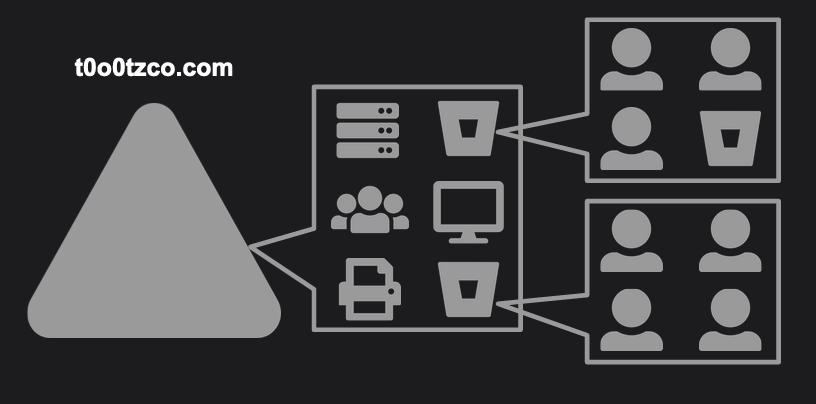
Objects
An object, within Active Directory, is basically a node or a piece of data within the network. There are two types of Objects - “resource objects” commonly printers , servers , and other shared resources within the network ; and “Security Objects” such as users , groups , computers , etc. To put it in simple terms an object is what’s “there”.
Domains
Domains are at the core of the Active Directory Structure. Domains can contain Objects as well as OUs. Suppose we have an organization “t0o0tz Co.", “t0o0tz Co.” has R&D, Sales, and Marketing departments. For Concept comprehension purposes let’s assume They have Domains named R&D, Sales, and Marketing.
Domains follow DNS naming conventions. Using our example earlier - Our organization “t0o0tz Co.” has a top level domain t0o0tzco.com as well as subdomains R&D.t0o0tzco.com, Sales.t0o0tzco.com, Marketing.t0o0tzco.com
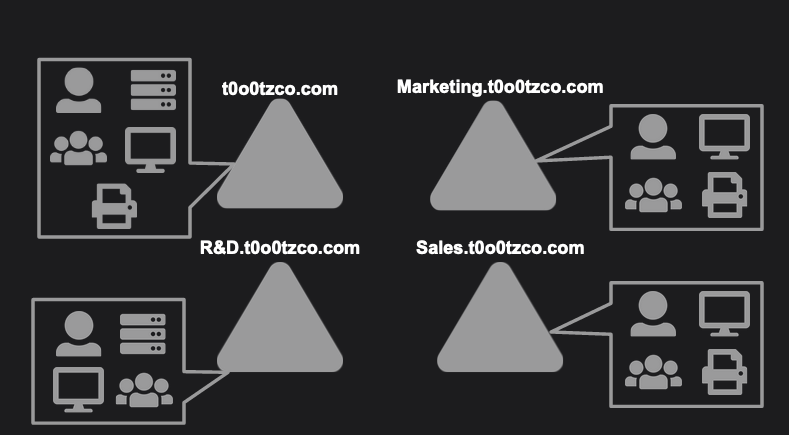
Organizational Units (OU)
Organization Units or OUs are buckets used to organize Objects within Domains. An OU can hold an object and can even hold a different OU. Organizational Units can be used to differentiate between objects with the same name, or to provide specific authorizations to certain groups.
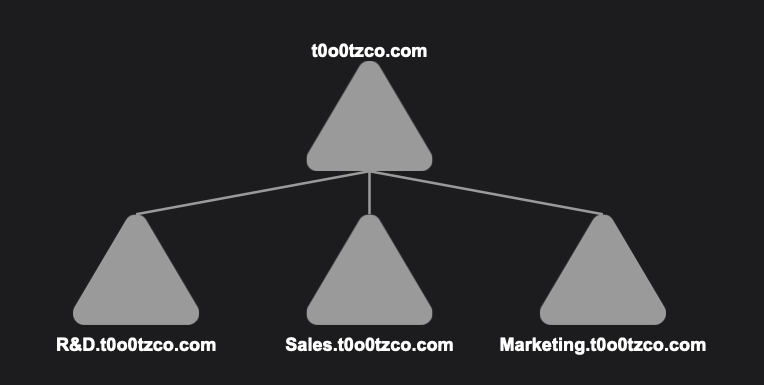
Trees
Trees are a hierarchical collection of Domains with a continued namespace. All Domains within a Tree share a network configuration, global catalog, and schema - any Domain added to the Tree is automatically trusted by every other Domain. Trees follow DNS standards for organization.
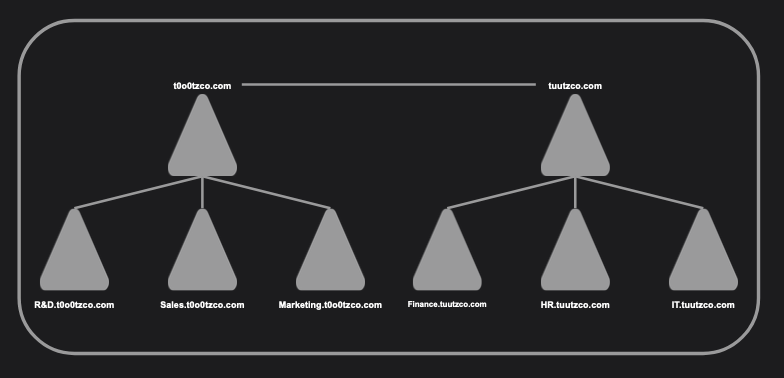
Forests
A Forest is a hierarchical collection of Trees. Some networks will contain more than one forest. If this is the case admins within “Forest A” are not automatically able to access “Forest B”
Active Directory Services
Active Directory Services provide further functionality to Active Directory. In terms of Cybersecurity understanding these services is crucial.
Domain Services
Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS) offer the core service to Active Directory. Domain Services centrally store data, is used for search functionality, manages communication between users and the domain, and provides login authentication.
Certificate Services
Active Directory Certificate services (AD CS) provides generation, management, and distribution of security certificates.
Lightweight Directory Services
Active Directory Lightweight Directory Services (AD LDS) can be thought of as the younger sibling of AD DS. AD LDS and AD DS share the same code base so they are fairly similar; however, AD LDS is not as full featured as AD DS. This lack of features (hence the “Lightweight”) allows AD LDS to run in multiple instances on a single machine.
AD LDS similar to AD DS stores directory data in a central data store using Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP). LDAP is a way to speak to Active Directory. It is a cross platform protocol which stores objects, like usernames and passwords, and shares them to other nodes in the network. A benefit of LDAP is its ability to be understood by many different identity and access management solutions.
Federation Services
Active Directory Federation Services (AD FS) is used for authentication of users across a multitude of applications using Single Sign On (SSO). AD FS has become increasingly popular thanks to the “Journey to Cloud” initiatives.
Rights Management
Active Directory Rights Management (AD RMS) provides a sort of data loss prevention, encrypting content to limit access and sharing outside of the organization.
Other Key AD Terms
Domain Controller
Domains are controlled by a Domain Controller. Domain Controllers are responsible for authentication, edits, object permissions, and modifications in a Domain.
Global Catalog
A database containing information on all objects within a forest regardless of which Domain the object is in.
Schema
Rules that govern objects as well as attributes within AD DS
Replication Service
Ensures that all domain controllers have the same global catalog & schema